NOVO BIOTIC BROILER
ANIMAL HEALTH PROBIOTICS IN BROILER
Problem Silent Tsunami
Antibiotics began to fail. Scientists haven't launched a new molecule since 1987, and resistant bacteria are already causing more than 750,000 deaths each year. 106 million new cases/year are seen. This figure is expected to rise dramatically if radical measures are not taken. The consequences of total resistance will be devastating. More than 60% of populations in some areas contain multidrug-resistant bacteria in the normal bacterial flora. It is estimated that 214,000 newborns die each year from blood infections (sepsis) caused by resistant bacteria – this represents at least 30% of sepsis deaths in newborns.
Antibiotic resistance has become one of the biggest threats to global health
Antimicrobial resistance (AMD) is a global health threat, with antimicrobial use in animal production and AMD being a contributory source. Poultry is one of the most widely consumed types of meat worldwide. Poultry flocks are often raised under intensive conditions using large quantities of antimicrobials to prevent and treat disease as well as to stimulate growth. Antimicrobial resistant poultry pathogens can lead to treatment failure, resulting in economic losses, but can also be a source of resistant bacteria/genes (including zoonotic bacteria) that can pose a risk to human health. The researchers estimate that globally, the average annual consumption of antibiotics is 148 mg/kg per kilogram of chicken produced.
AGPs have been banned in more than 30 countries around the world due to concerns for human health and the emergence of superbugs or the emergence of multiple antibiotic-resistant bacteria. In 35 countries, there is a veterinary prescription requirement.
TOP 12 AMR POULTRY PATHOGENS
- Escherichia coli
- Salmonella Pullorum / Gallinarum
- Clostridium perfringens
- Mycoplasma spp.
- Pasteurella multocida
- Avibacterium paragallinarum
- Gallibacterium anatis
- Ornithobacterium rhinotracheale (ORT)
- Bordetella avium
- Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
- Riemerella anatipestifer.
Studies reveal that resistance increases over time for S. pullorum / Gallinarum, M. gallisepticum, and G. anatis. Among enterobacteria there is a prevalence of resistance over 80% for ampicillin, amoxicillin and tetracycline. Gram negative has the highest levels of phenotypic resistance to ORT co-trimoxazole, enrofloxacin, gentamicin, amoxicillin and ceftiofur with high AMD levels. (all exceeding 50%)
Salmonella is a zoonotic pathogen that is easily transmitted from animal to human through the consumption of contaminated food. The prevalence of Salmonella associated with poultry and poultry meat products is well documented and has both public health and economic implications. The estimated total annual cost of Salmonella, which does not cause typhoid, is more than $14 billion in the United States alone. About 41,930 cases of non-typhoid foodborne salmonella are confirmed each year, and an estimated total of 1 million foodborne salmonella cases go unreported.
E. Coli Resistance : recent studies show that 90% of E. coli strains isolated from broiler chickens are resistant to at least one antibiotic. 15.5% were colistin-resistant, 2.2% were broad-spectrum β-lactamase producers, and 2.2% were multidrug resistant to four antibiotic classes.
Clostridium perfringens, a soil-borne organism, is found in dust, faeces, feed, poultry litter and intestinal contents in almost every poultry farm and causes Necrotic enteritis .
Studies generally reveal that isolated strains are resistant to gentamicin, streptomycin, oxolinic acid, lincomycin, erythromycin and spiramycin. The prevalence of resistance to other antibiotics is also high: rifampicin (34%), chloramphenicol (46%), spectinomycin (50%), tylosin-fosfomycin (52%), ciprofloxacin (58%), norfloxacin (67%), oxetracycline (71%) , flumequin (78%), enrofloxacin (82%), neomycin (93%), colistin (94%), pefloxacin (94%), doxycycline (98%), and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (98%).
Periodic observation of trends in resistance patterns is appropriate because of the possibility that C. perfringens is a source of resistance genes that are passed on to other bacterial species. There is substantial potential for future therapeutic challenges if care is not taken not to select multiresistant organisms.
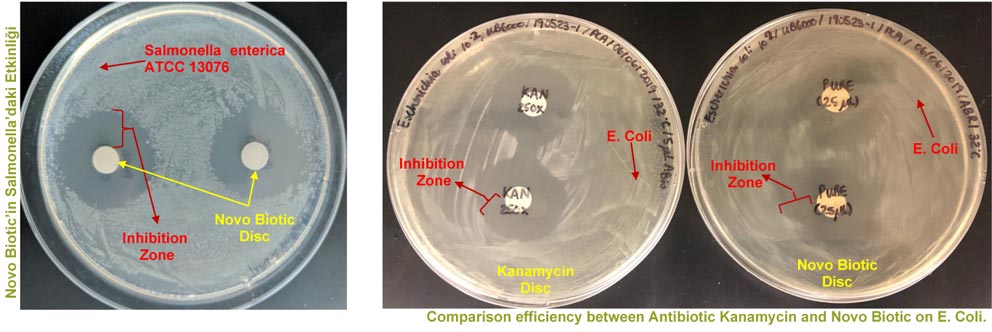
NOVO BIOTIC ®
Novo Biotic Bacillus Amyloliquefaciens strain FD777 was selected based on its survival in the Gastro-intestinal tract with its ability to withstand high pH, low pH and high concentrations of bile acids. Spores are resistant to physical and environmental factors such as heat, drying and UV radiation, which allows them to maintain their vitality and desirable properties during feed pelleting, storage and processing.
The combination of 34+ Natural Antibiotics in Novo Biotic works synergistically to denature DNA, RNA, enzymes and stop all activase metabolism mitochondria and inner cell respiration within pathogenic bacteria. It acts as a preventive and therapeutic.
Antibiotics genetically elicited and produced by Bacillus Amyloliquefaciens FD777 34+
|
|
These antibiotics are thermostable and the causative agent of necrotic enteritis in poultry is Clostridium perfringens, Bacillus Amyloliquefaciens, Staphylococcus, Enterococcus, Listeria, Mycoplasma and Salmonella species, Pseudomonas etc. It has antimicrobial activity against potential pathogens of animals such as
- Replaces Antibiotic Growth Supplements
- It is used as a preventive & therapeutic for bio-solution purposes.
- Lowers mortality
- Replaces Probiotics and Water Disinfectants
- Reduces FCR
- Increases Body Weight Gain
- Increases EPF
DIRECT EFFECTS
INDIRECT EFFECTS
Usage Areas
Drinking Water – Protection
- Broiler First Week: Add 3 L NOVO BIOTIC ® to 1000 L drinking water
- Broiler second week to slaughter: Add 1 L NOVO BIOTIC ® to 1000 L drinking water
Dilution can be done with the Dosatron system, ideally in the reserve tank. For best results, keep animals drinking water enriched with NOVO BIOTIC ® constantly .
Stop water acidifiers, AGPs in feed, Probiotic and water disinfectants during NOVO BIOTIC ® dosing .